搜索网站、位置和人员

新闻与活动 活动信息
西湖名师论坛第九十五期 | 李劲松: Sperm-like Stem Cell-mediated Genome Editing
时间
2021年5月11日(周二)
下午16:00-17:30
地点
西湖大学云栖校区5号楼一楼学术报告厅
主持
西湖大学生命科学学院PI 常兴
受众
全体师生
分类
学术与研究
西湖名师论坛第九十五期 | 李劲松: Sperm-like Stem Cell-mediated Genome Editing
时间:2021年5月11日(周二)下午16:00-17:30
Time:4:00-5:30 PM, Tuesday, May 11th, 2021
地点:西湖大学云栖校区5号楼一楼学术报告厅
Venue: Lecture Hall, 1F, Building 5, Yunqi Campus
主持人:西湖大学生命科学学院PI 常兴
Host: Dr. Xing Chang, PI of School of Life Sciences, Westlake University
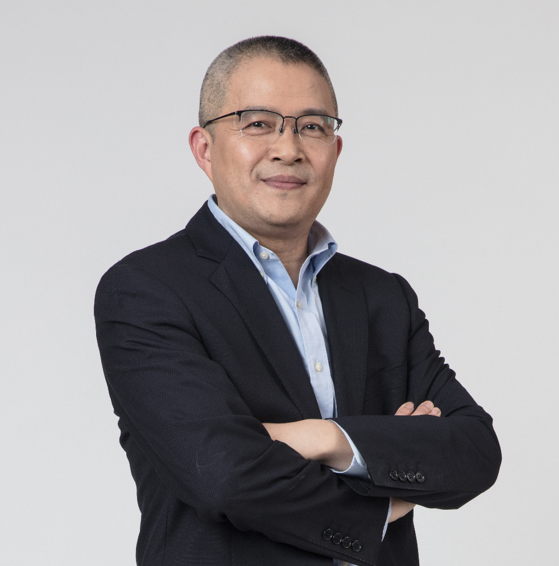

主讲人/Speaker:
李劲松,中国科学院分子细胞科学卓越创新中心(生化与细胞所)研究员
细胞生物学国家重点实验室,主任
Jinsong Li, Professor, Director of State Key Laboratory of Cell Biology, CAS Center for Excellence in Molecular Cell Science, Shanghai Institute of Biochemistry and Cell Biology (SIBCB), Chinese Academy of Sciences
Dr. Li obtained his PhD degree from Institute of Zoology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, in 2002 and followed by postdoctoral training at Rockefeller University before joining SIBCB in 2007. His research mainly focuses on stem cells and embryonic development. He has made fundamental contributions to the establishment of androgenetic haploid embryonic stem cells (also termed “sperm-like stem cell”) that can be used as sperm replacement for efficient production of semi-cloned mice (so called semi-cloning (SC) technology). Dr. Li has made great efforts to promote the applications of SC technology, which can be used as a unique tool for genetic analyses in mice, including efficient generation of mouse models carrying defined point mutations related to human developmental defects; one-step generation mouse models that mimic multiple genetic defects in human diseases; and medium-scale targeted screening of critical genes or critical nucleotides of a specific gene involved in a developmental process. Most recently, Dr. Li initiated and is promoting a huge project to tag every protein in mice based on sperm-like stem cell-mediated SC technology (genome tagging project, GTP), which may enable the precise description of protein expression and localization patterns, and protein–protein, protein–DNA and protein–RNA interactions in development/ aging, physiological and pathological conditions.
报告题目/Title:
Sperm-like Stem Cell-mediated Genome Editing
讲座摘要/Abstract:
From androgenetic haploid blastocysts derived by injection of sperm into enucleated oocytes, we generated mouse androgenetic haploid embryonic stem cells (AG-haESCs) that can support full-term embryonic development upon injection into oocytes, leading to the production of semi-cloned (SC) mice (semi-cloned technology). However, one major drawback of this technology is the very low birth rate of healthy SC mice (2% of total SC embryos transferred). Recently, we established AG-haESCs carrying H19-DMR and IG-DMR deletions (DKO-AG-haESCs) that can efficiently support the generation of SC pups at a rate of 20% (“sperm-like stem cell”). Sperm-like stem cell-mediated SC technology, combined with CRISPR-Cas9 technologies, enables one-step generation of mouse models that mimic multiple gene dosage reduction in human Myotonic Dystrophy type 1 (DM1); identification of novel mutations involved in human neural tube defects; medium-scale targeted screening of critical factors involved in bone development; base mutagenesis of a specific protein-coding gene to identify critical amino acids for protein function in vivo; and efficient generation of mice carrying tagged proteins at genome-scale (Genome Tagging Project, GTP). Moreover, we established haploid ESCs from monkey and human parthenogenetic embryos and most recently human artificial spermatids from androgenetic embryos. In summary, haESCs provide powerful tools for genetic analyses in mammals at both cellular and organismal levels.
The lecture will be given in Chinese.
讲座联系人/Contact:
科技合作部 毕老师
biguanying@westlake.edu.cn